每个Broker上都有一个ReplicaManager,它管理每个Partition的数据同步逻辑,因为每个Partition都会存在副本,从而在Broker中的TopicPartition可能是Leader或者Follower。
当它是Leader时,就需要处理来自Producer的请求,写入log数据,同时等ISR集合同步完成,如果是Follower,就需要同步来自Leader的log数据,保持数据同步。
在ReplicaManager中,就会开启同步Follower线程来FetchMessage。在ReplicaManager中会调用makeFollowers来处理同步Leader数据的逻辑。
1 | |
源码注释了什么情况下会将partition变成Follower,makeFollowers这个方法会在handleLeaderAndIsrRequest中被调用
1 | |
makeFollowers主要的steps:
-
partitionsToMakeFollower 里面包含的是Leader发生改变的partition
-
接下来removeFetcherForPartitions会从fetcher线程中移除对partition的同步,为了保证从新Leader中从正确的位置开始同步
-
completeDelayedFetchOrProduceRequests,完成那些之前异步的Fetch操作
-
之后会将同步的信息包装成Map[TopicPartition, InitialFetchState],里面包含的信息如下代码,之后将此信息放进Fetcher线程中进行同步
1 | |
Fetch 线程同步
replica线程在启动后,就会进行同步操作,ReplicaFetcherThread会调用doWork():
1 | |
1. maybeTruncate()
maybeTruncate会将Leader Offset改变的follower进行高水位或者LeaderEpoch进行重新平衡,先不深入LeaderEpoch
1 | |
truncateToHighWatermark会将partitionsWithoutEpochs中所有处isTruncating状态的local partition's offset更新成新Leader Partition高水位的offset,因为有些处于Truncating的partition可能Log end offset已经大于新Leader的高水位,此时进行截断,从新Leader的高水位开始进行同步
2. maybeFetch
1 | |
maybeFetch主要是组装fetchRequest:
1 | |
然后发送请求到Leader所在的Broker,之后进行follower副本offset的更新。processFetchRequest中将fetchRequest放入sender线程中进行请求
1 | |
当response返回了数据,调用processPartitionData更新follower的log end offset,其中processPartitionData会进行partition.append操作;当写完本地log后,更新partitionState.updateAndMoveToEnd,
1 | |
- maybeUpdateHighWatermark
- 如果leader的partition高水位发生改变,就更新follower的高水位
- maybeIncrementLogStartOffset
- 如果leader的logStartOffset更新了,也需要更新本地副本的logStartOffset。
3. completeDelayedFetchRequests
1 | |
刚开始还有个疑问,为什么follower中还有completeDelayedFetchRequests操作,刚看了KIP-392,其中描述了避免跨机房从Leader中获取消息外,Kafka支持从就近的Replica中获取消息,从而就会存在consumer fetch request from follower,于是就会存在delayedFetch操作,从而当follower的高水位更新后,避免因replica.fetch.wait.max.ms超时才响应,而是在更新高水位后就立即尝试响应
-
HandleFetchRequest
当Broker server收到fetchRequest后,KafkaApis会将其mapping到handleFetchRequest的方法中来处理,下面来详细介绍其处理方式:
1 | |
其主要就是调用replicaManager.fetchMessages:
- ReplicaManager 处理 Fetch 请求看起来比较清晰,先是readFromLog,将topicIdPartition请求的logReadResult读取出来
1 | |
核心是在read里面,先是getPartition,然后根据fetchInfo从相应的partition中fetchRecords
1 | |
fetchRecords会先readFromLocalLog,然后执行updateFollowerFetchState
1 | |
readFromLocalLog先不介绍日志层,我们看获取到logReadInfo以后,执行了哪些更新操作
1 | |
- replica执行updateFetchState,更新follower Replica的offset信息
- maybeExpandIsr判断如果replica的offset已经追赶上leader的endOffset,就提示可能要更新Isr集合
注释解释了当 LEO >= HW && followerEndOffset >= leaderEpochStartOffsetOpt ,就可以加入ISR
1 | |
- maybeIncrementLeaderHW会判断所有的replica的最小logEndOffset值,或者Isr集合有变化时,来判断是是否更新高水位
1 | |
- 如果leader的低水位(所有replica的最小startLogOffset)或者高水位有变化,就tryCompleteDelayedRequests
- 当处理完remote replica的所有更新后,如果满足以下条件,就立即返回:
1 | |
- 否则就new DelayedFetch,将其放进延迟队列中,异步等待请求数据完成再发送
- 在调用结束后,会执行一次所有的DelayOperation
异常情况:
当Follower出现OFFSET_OUT_OF_RANGE异常时,则需要根据情况来进行重新fetch,下面是Kafka解释出现OUT_OF_RANGE的case:
- 当ISR集合中的Replica都下线了,那么Follower变成了Leader,不久后old Leader又复活变成了Follower从新的Leader上进行同步,发现old Leader的logEndOffset>newLeaderEndOffset,此时会将old leader的log进行截断,从新Leader的EndOffset后开始同步
1 | |
- Follower的logEndOffset< Leader logStartOffset,则清空Follower的Offset,从Leader logStartOffset开始同步
1 | |
下面总结一下fetch的流程:
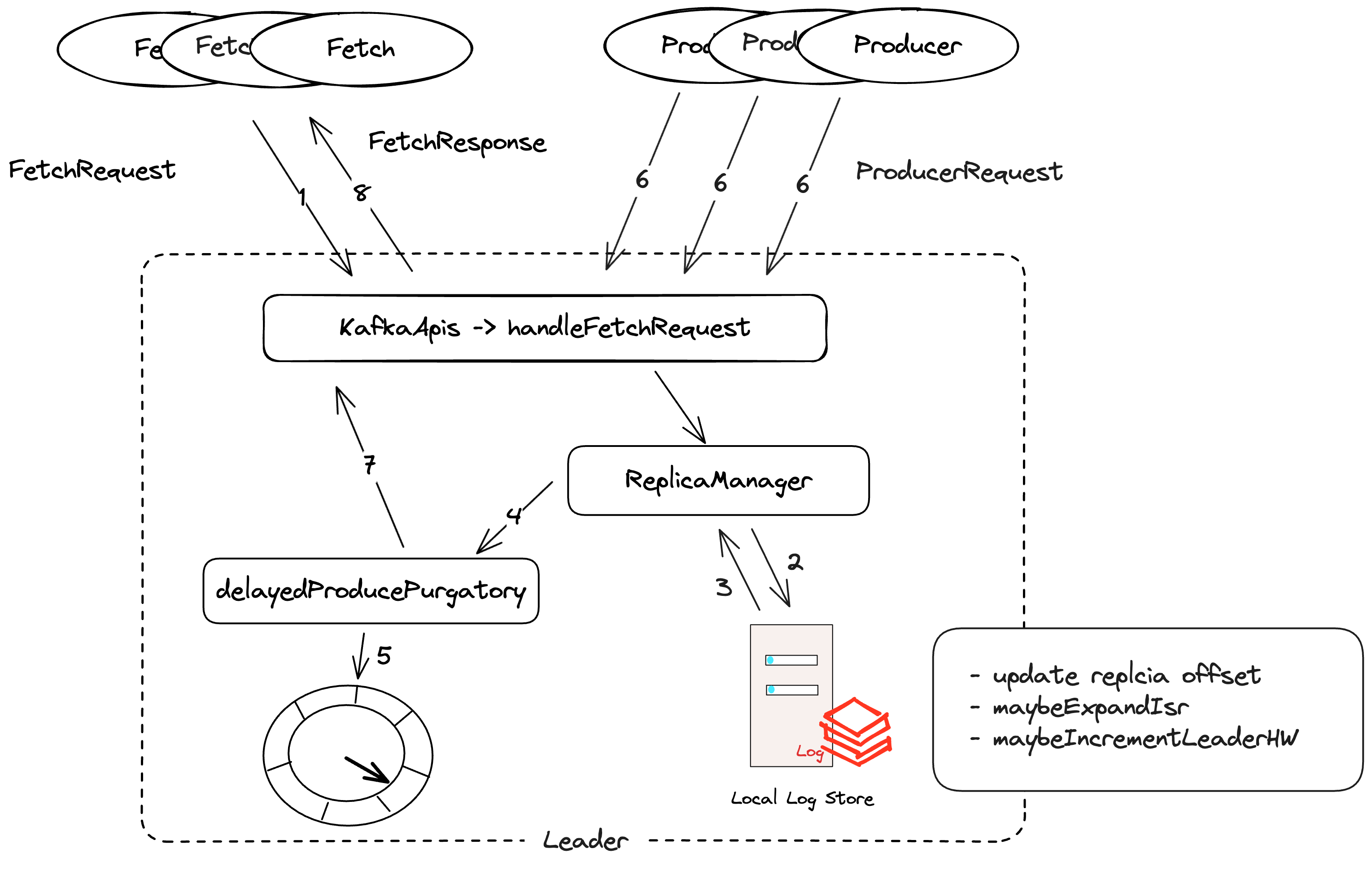
- Follower副本发送FetchRequest,从对应分区中获取消息
- 当请求到对应Partition的Broker中,会从日志存储中读取数据,更新remote
replica offset,检测是否需要更新ISR集合、HW等 - 之后ReplicaManager为FetchRequest生成DelayedFetch对象,交由
delayedFetchPurgatory管理 - 准备FetchResponse返回给客户端
- 执行一次DelayOperation,比如看DelayProduce是否已经完成
- 客户端收到response后更新本地的partition的数据:HW、LEO